General Glassware
General glassware encompasses essential laboratory tools used for a wide range of tasks, from mixing and heating to measuring and storing liquids. Made from durable materials like borosilicate glass, these versatile items, including beakers, flasks, test tubes, and pipettes, are fundamental in educational, research, industrial, and clinical laboratories. Their durability, variety, and ease of use make them indispensable for accurate and efficient lab work.
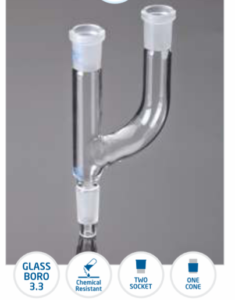
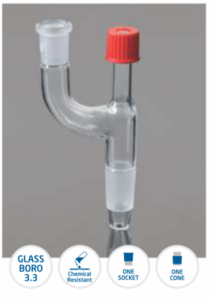
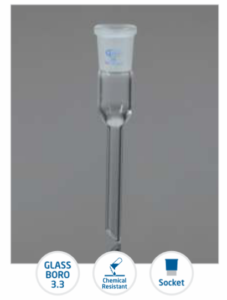
Adapter
A Laboratory Adapter is a specialized device used to connect and join different glassware components, such as flasks, condensers, and tubes, in laboratory settings. It ensures a secure, airtight seal, allowing for safe and efficient transfer of chemicals, gases, and other substances during experiments and procedures.
All adapters come in dif ferent shapes and sizes are manufactured from ASTM E 438 TYPE 1 Class A Boro 3.3 Glass.
that meets DIN/ISO 3585 & USP Type requirement.
Beakers
A Beakers is a cylindrical, flat-bottomed laboratory glassware container used for measuring, mixing, and heating liquids, chemicals, or biological samples. It typically has a lip or spout for easy pouring and is made of heat-resistant materials like borosilicate glass or plastic. Beakers are essential tools in scientific research, education, and quality control, providing a versatile and reliable vessel for various laboratory applications.
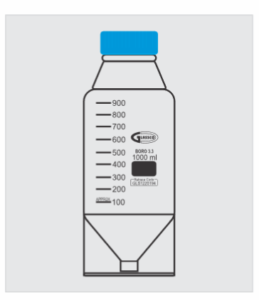
Bottle
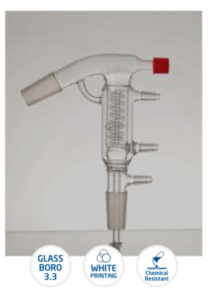
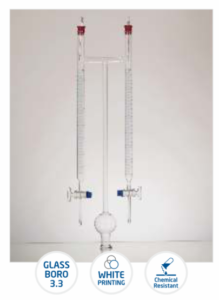
Column
Condenser
Crucible
Desiccator
Dishes
Disposable
Distillation
Extraction Apparatus
Filtration
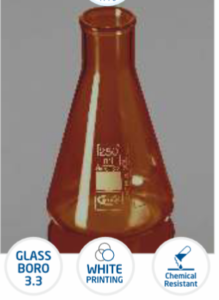
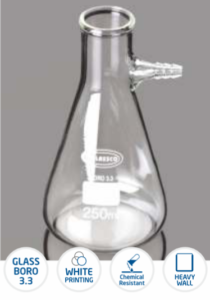
Flask
Funnels
Lab funnels are cone-shaped laboratory tools used to pour liquids or solids into small openings or containers without spilling or contaminating the contents. They are typically made of plastic, glass, or stainless steel and come in various sizes to fit different applications. Lab funnels are essential for accurate and precise transfer of materials in laboratories, minimizing waste and ensuring cleanliness.
Joints
Get in Touch Today!
Who We Are
We are a leading provider of life science solutions, offering a wide range of high-quality products and innovative services. With 20 years of experience, we support pharmaceutical development, manufacturing, and research, focusing on customer satisfaction and sustainability.